Hardware Tools (Chapter 14)
Remote production has a unique set of challenges that can impact the quality and efficiency of productions. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective strategies to overcome them and ensure successful remote production operations.
In remote production, challenges can arise at any stage—from initial setup and live broadcasting to post-production and distribution. For example, the venue may provide internet access which tests fine during your pre-production walkthrough and then during the event hundreds of smartphones start using the same WiFi connection. These issues can affect technical aspects, such as video and audio quality, as well as organizational dynamics, including team collaboration and workflow management. Addressing these challenges as early in the process as possible (i.e. during the site survey) is essential not only to maintain the high standards expected in professional broadcasts but also to leverage the full potential of remote production capabilities.
Bandwidth Issues
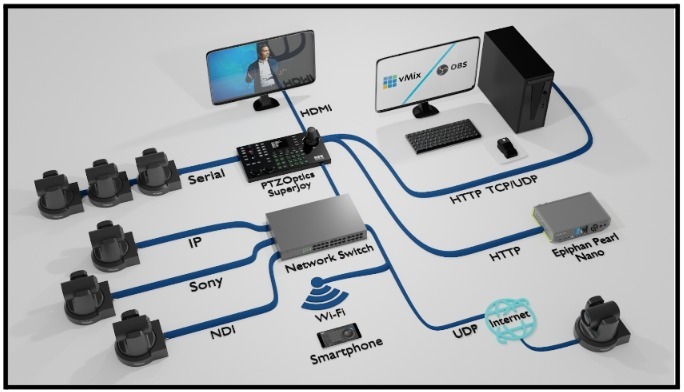
In remote production, several bandwidth-related challenges can significantly impact the quality and reliability of broadcasts. Network congestion, as mentioned above, often, leads to dropped frames and increased latency. You can avoid network congestion by setting up your own private network and using a VLAN (Virtual LAN) for your highest priority video and audio sources. Inadequate upload speeds are a critical issue, especially for uploading large video files or streaming high-quality video, resulting in poor stream quality and interruptions. Network bonding solutions or services such as Speedify allow you to create a stronger overall internet connection by bonding together sources such as hardwired ethernet, WiFi and cellular connections (even from multiple cellular networks). Speedify can help reduce unreliable internet connections which can fluctuate or drop intermittently, disrupting live broadcasts and affecting team collaboration. Bonding solutions can also help reduce the risk of bandwidth throttling by internet providers during high usage periods can unexpectedly reduce bandwidth availability, impacting both live and post-production workflows.
Additionally, latency can delay audio and video streams, crucially affecting live event timing and synchronization. Variable bitrate streaming may seem like a good idea in low-bandwidth environments but the variability can introduce latency between sources. Consider using constant bitrate connections for each IP-connected device.
Remote Production Tip for Troubleshooting IP Video Latency and Synchronizing Multiple IP Video Sources
When dealing with multiple IP cameras in a remote production setting, it’s crucial to synchronize the video feeds and audio to avoid discrepancies that can detract from the professionalism of the stream. A solution to this involves using a common Network Time Protocol (NTP) server to ensure all devices, including cameras and PCs, are properly synchronized without introducing additional latency.
To begin, identify and select a Network Time Server that corresponds with your network equipment or is geographically close to your location to minimize latency. For example, a production based in Philadelphia might choose a server in New York or Virginia. After selecting a server, configure each camera through its web interface by setting the NTP settings under the “Network” section, adjusting the time zone, enabling NTP Time Sync, and specifying the server address and time interval.
Similarly, for PCs, whether Windows or Mac, adjust the system’s time settings to synchronize with the same Network Time Server. This ensures that all video feeds from the cameras are synchronized to within 30 ms as tested, significantly reducing the chances of video latency and ensuring smooth, synchronous playback.
If audio synchronization is also required, simply route the audio output through the line-level input on the cameras to align the audio feed with the video feeds.
This method not only streamlines the synchronization of video and audio across multiple sources but also mitigates potential timing discrepancies between devices, ensuring a coherent and synchronized production output.
To address these challenges effectively, it is essential to engage in careful planning and implement contingency measures such as securing backup internet connections, using dedicated lines, and dynamically adjusting broadcast quality based on real-time bandwidth assessments. These strategies help maintain consistent broadcast quality and ensure that remote productions meet professional standards and fully leverage modern broadcasting technology.
Strategic Approaches to Overcoming Challenges in Remote Production
Successfully navigating the complexities of remote production requires not only addressing immediate technical and organizational issues but also adopting strategic approaches that leverage industry standards and emerging technologies. This section explores how adopting standards and integrating new technologies can provide robust solutions to the challenges faced in remote production.
The journey through the challenges and solutions in remote production underscores the importance of resilience and adaptability in the media sector. By understanding and addressing the complexities associated with remote production, teams can harness its full potential to produce engaging, high-quality content that meets the demands of modern audiences. The strategic adoption of new technologies and continual improvement of processes will ensure that remote production remains a vital and effective approach in the ever-evolving landscape of broadcast media.