Managing Multiple Studios
Mastering Remote Camera Adjustments with PTZOptics Hive
Introduction to Remote Camera Setup
Setting up your camera for remote production involves a few crucial steps to ensure that you achieve optimal image quality and functionality. Whether you are managing live events, broadcasts, or remote video shoots, understanding how to manipulate camera settings remotely can elevate your production value significantly. This blog post guides you through the process of adding and adjusting your camera using PTZOptics Hive.
Hive supports over 400 PTZ cameras. You can check out our support camera list here.
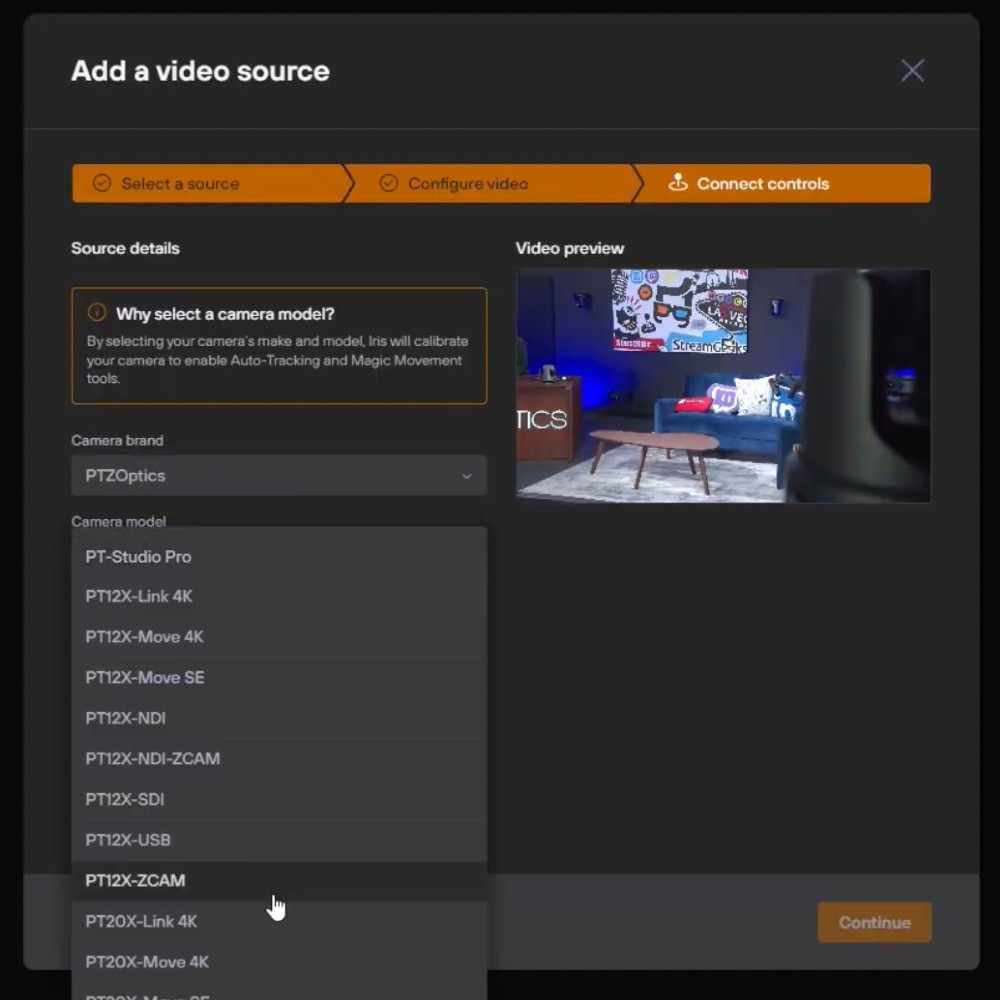
Step 1: Adding Your Video Source
The first step in remote camera management is adding your camera as a video source in PTZOptics Hive. Select the correct driver from our supported camera list to ensure full compatibility and functionality. If your camera is not listed, a generic driver may be used, though specific functionality might be limited.

Step 2: Connecting Your Camera
Once the appropriate driver is installed, connect your camera to Hive, either directly through a local area network (LAN) or remotely over the internet. This flexibility allows for seamless control, whether you are on-site or managing the production from a different location.
Step 3: Naming Your Camera
For ease of management, especially when dealing with multiple cameras, naming each camera can simplify your workflow. This step is crucial for quickly identifying and switching between different video feeds during live production.
Adjusting Image Settings
The Hive interface provides a comprehensive suite of image settings that you can adjust to enhance your video output:
- Iris: Control the camera’s aperture to adjust how much light enters the lens.
- Shutter Speed: Modify how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light, impacting motion blur and exposure levels.
- Gain: Adjust the camera’s sensitivity to light, useful in low-light conditions.
These settings are essential for color matching multiple cameras, ensuring a consistent look across all feeds.
PTZ Camera Control Settings
The pan, tilt, and zoom (PTZ) controls are adjustable to set the movement speed of your camera:
- Speed Settings: Adjust how quickly or slowly the camera moves in response to PTZ commands, allowing for smooth transitions and precise framing.
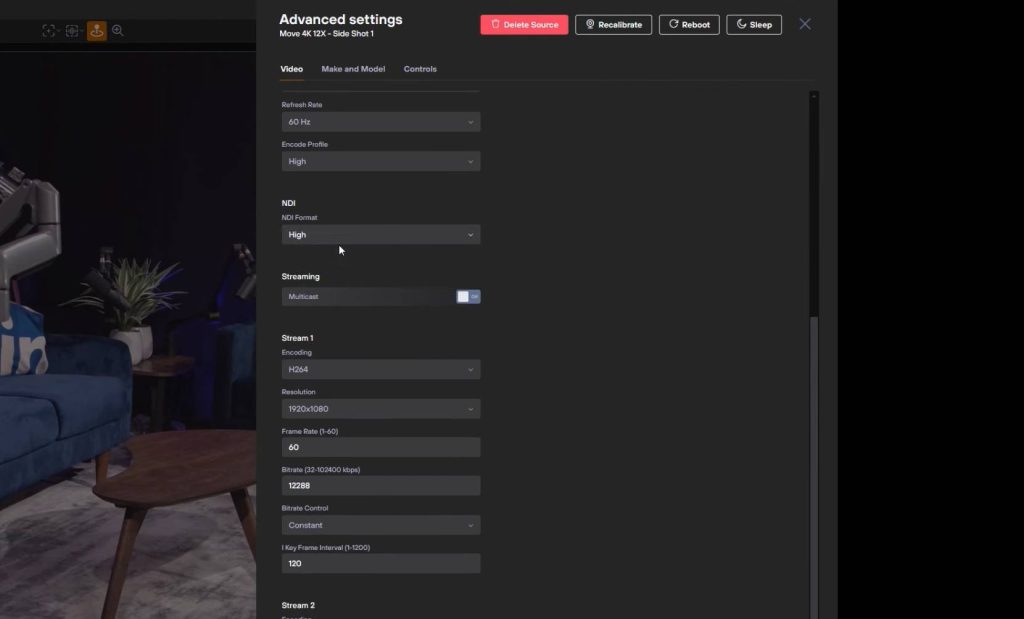
Advanced Settings for Stream Quality
In the advanced settings menu, you can fine-tune your streaming output to match your production needs:
- Bitrate: Adjusts the amount of data transmitted per second in your video stream, which can be lowered to adapt to limited bandwidth or increased for higher quality.
- Frame Rate: Choose how many frames per second (fps) your stream outputs, affecting how smooth the motion appears.
- Resolution: Set the dimensions of the video output, which can range from standard definition to high-definition formats.
Adjusting these settings may require a reboot of the camera to apply changes, especially when altering the stream’s bitrate or resolution.
Optimizing Bandwidth Usage
It’s crucial to adjust the bitrate in consideration of your available bandwidth. High bitrate settings offer better video quality but consume more bandwidth. In limited bandwidth scenarios, reducing the bitrate helps prevent streaming issues like buffering and loss of connection.
Conclusion
Remote camera adjustments via PTZOptics Hive empower producers and technical directors to fine-tune their video feeds remotely, ensuring that every aspect of the camera’s output meets the production’s visual standards. By understanding and utilizing these settings, you can dramatically improve the quality and professionalism of your broadcasts, making remote production not just feasible but also highly effective.